Real Info About Gross Profit Income Statement Deferred Tax Example
Gaap) and tax accounting, where the actual amount of taxes paid to the irs were less than the amount reported on the income statement.
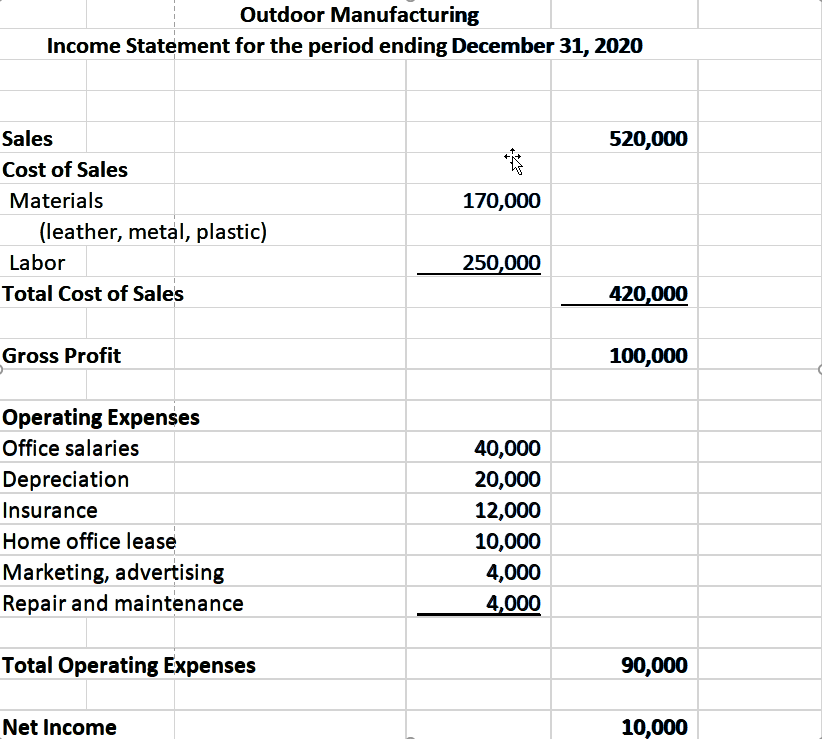
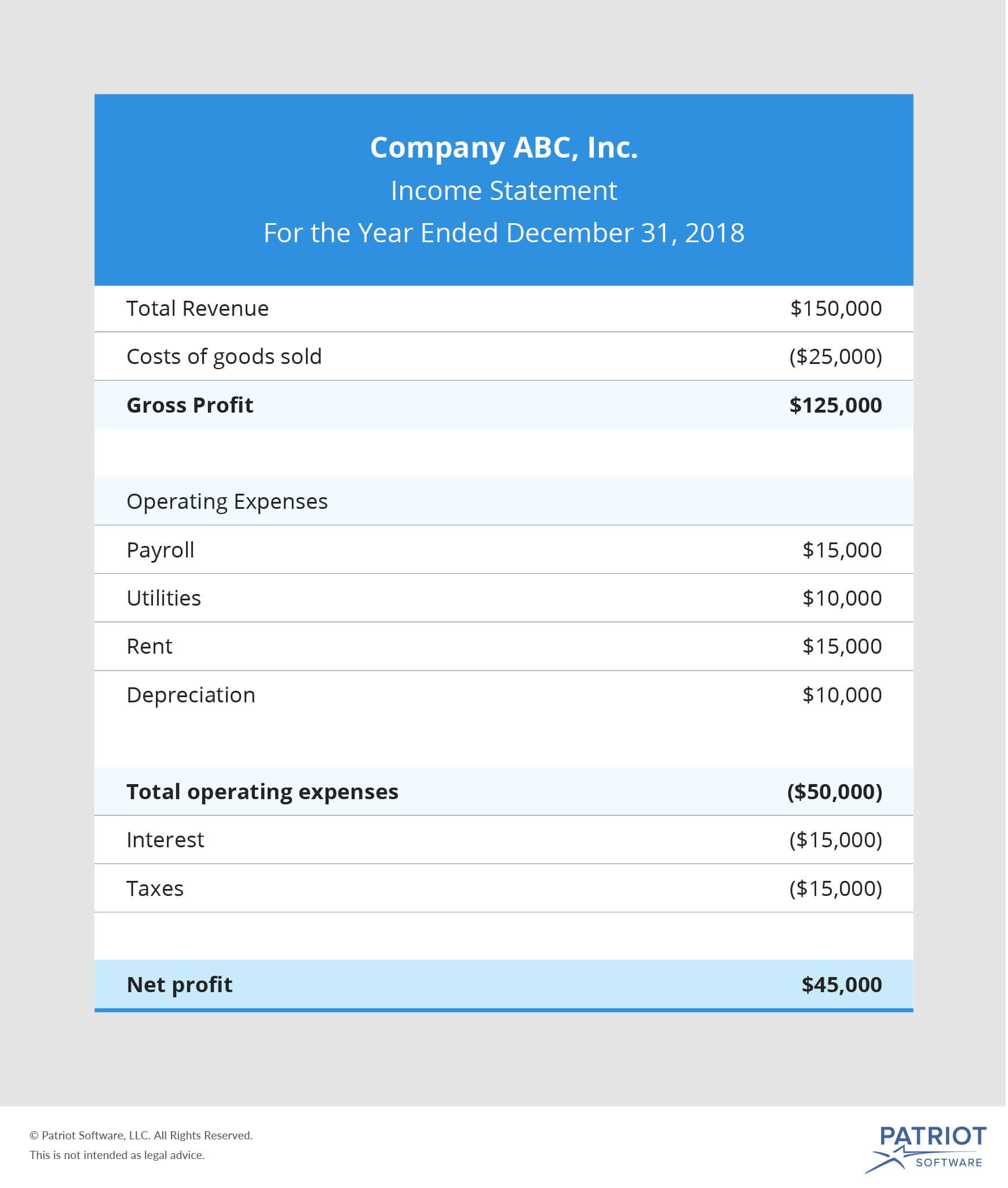
Gross profit income statement deferred tax example. It simply refers to the tax that is overpaid or owed by the company to the tax authorities. Whereas, for tax statements, tax payable refers to the amount charged on gross profit after depreciation. Amendments to ias 12 income taxes.
Income received in advance these are called timing differences. What creates a deferred tax. Other circumstances are described below.
A deferred tax liability (dtl) stems from temporary timing differences between the taxes recorded under book (u.s. (a) deferred income tax assets the group recognises deferred income tax assets on carried forward tax losses to the extent there are sufficient estimated future taxable profits and/or taxable temporary differences against which the tax losses can be utilised and that the group is able to satisfy the continuing ownership test. Generally, the income tax basis in a fixed asset is the purchase price less tax depreciation previously allowed under the applicable tax law.
Deferred income tax affects the tax outgo to the authorities for the financial year. In income statements, reported tax is a percentage of gross profit after depreciation. Its examples include an annual plan for the mobile connection, prepaid insurance policies, etc.
The deferred tax computation is as follows: Deferred gross profit (contains unrealized profit) = net accounts receivable (contains cost only) example of deferred gross profit. Abc international sells $100,000 of goods under a periodic payment plan.
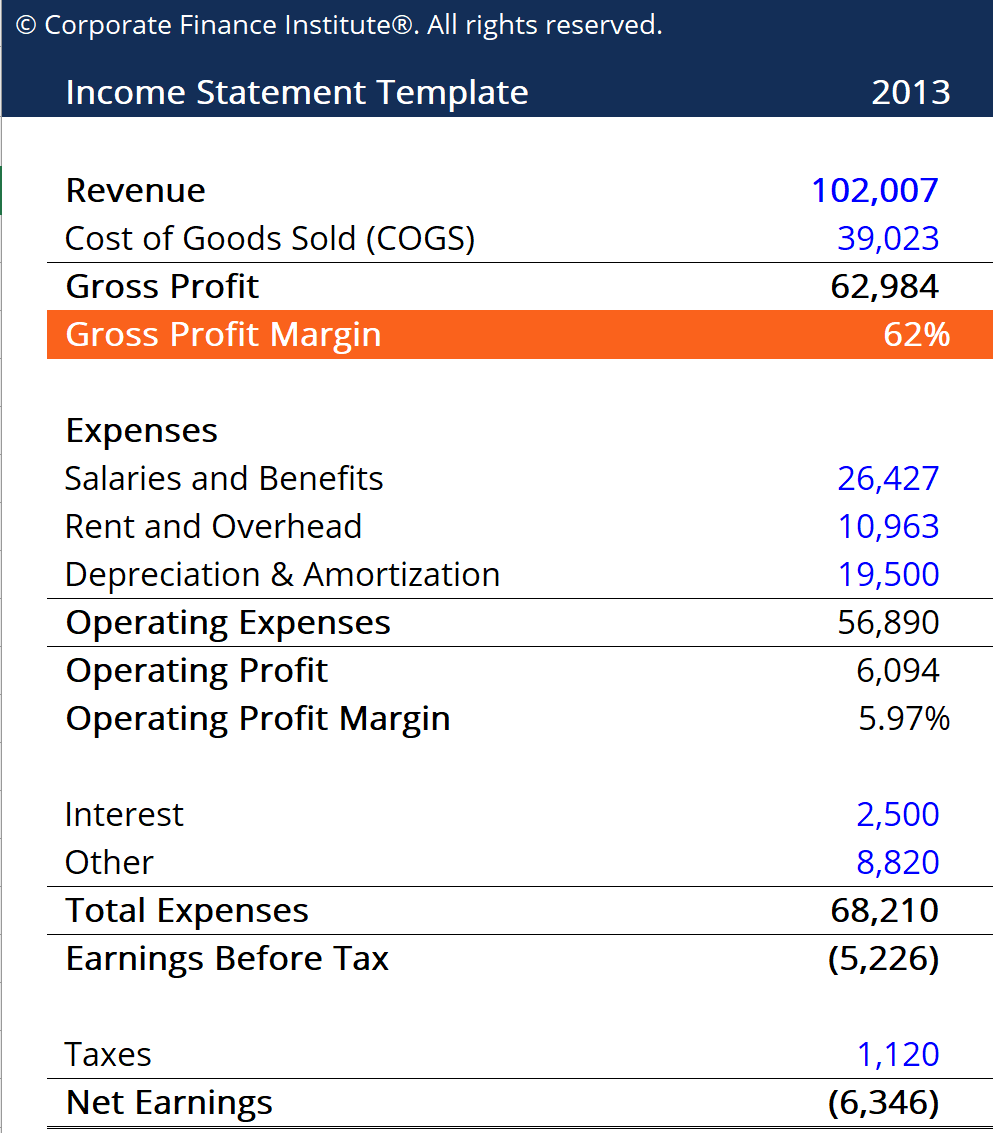
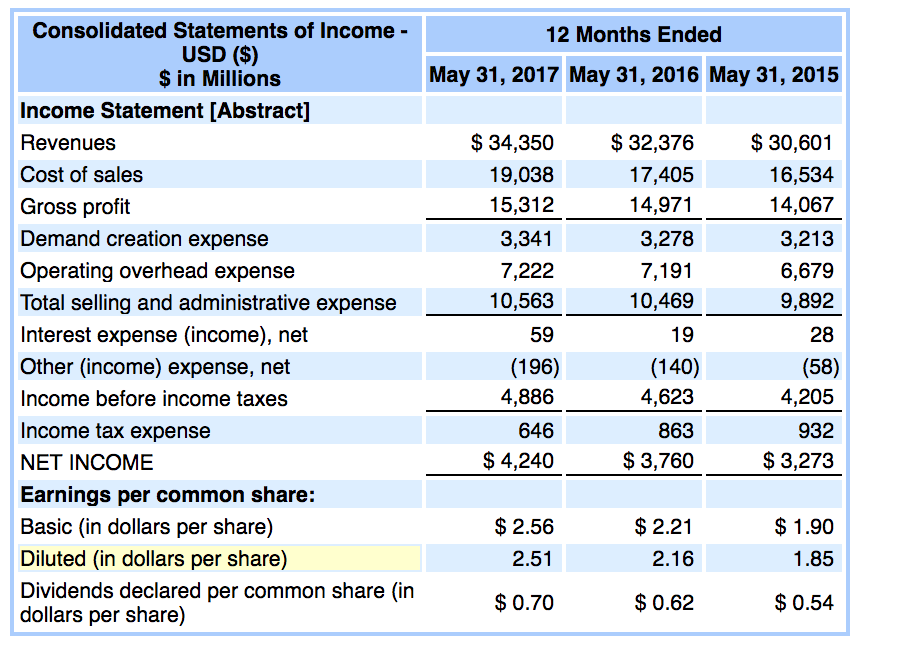
To calculate dtl, we use the following formula: As we have seen in the example, accounting for deferred tax then results in a further increase or decrease in the income tax expense. Distribution costs (9,000) (13,700) administrative expenses (20,000) (31,500) other expenses (2,100) (1,200) finance costs (8,000) (7,500) share of profit of associates.
First, calculate the gross profit percentage received on actual cash received. The timing of the cost recovery of the fixed asset may differ between the tax law for a particular jurisdiction and the applicable accounting rules, which can result in a deferred tax asset or. The capital allowances granted on this asset are:
Use the historical gross profit percentage as a guideline for your estimation. As we have seen in the example, accounting for deferred tax then results in a further increase or decrease in the income tax expense. Example of deferred revenue let us look at a detailed example of the accounting entries a company makes when deferred revenue is created and then reversed or earned.
A deferred income tax is a liability recorded on a balance sheet resulting from a difference in income recognition between tax laws and the company’s accounting methods. Therefore, the final income tax expense for each year reported in the statement of profit or loss would be as follows: Examples of deferred revenue deferred revenue or unearned revenue is the number of advance payments that the company has received for the goods or services that are still pending delivery or provision.
Current income tax charge (4,000) (4,000) (4,000) (4,000) (4,000) deferred income tax. It is merely the difference between gross profit in a profit & loss account and a tax statement. Accounts receivable (contains cost of sales + profit) less:
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_Gross_Profit_Operating_Profit_and_Net_Income_Oct_2020-01-55044f612e0649c481ff92a5ffff1b1b.jpg)




:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/TeslaQ2-19IncomeStatementInvestopedia-1466e66b056d48e6b1340bd5cae64602.jpg)

:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/TermDefinitions_DeferredTax_V2-d5ae6ed922204f7eaa8bfb6b7b4b7f44.jpg)